The advancements in automation in the operating room over the last few years have transformed medical practice, with implications for healthcare quality, patient safety, and overall efficiency. By integrating advanced technology, surgeons are now able to carry out precise, minimally invasive procedures that enhance patient outcomes, reduce recovery times, and minimize the risk of complications.
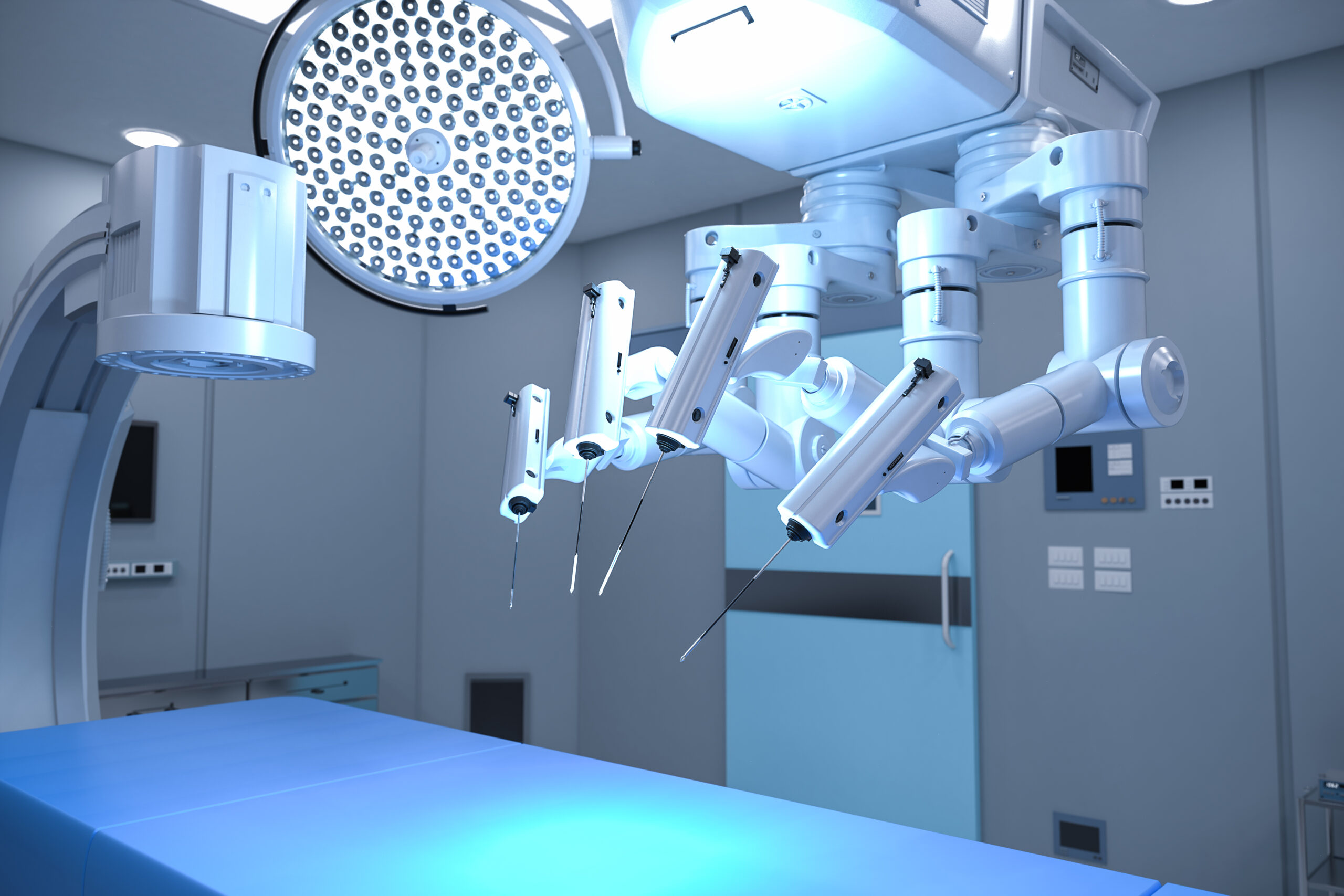
One of the most impactful advancements in this realm has been the evolution of robotic surgical systems. A pioneer example is the Da Vinci Surgical System, which provides 3D high-definition vision and special wristed instruments that bend and rotate with a degree of precision that surpasses the human hand. Such robotic systems have expanded the possibilities in numerous surgical specialties, from cardiothoracic and urologic procedures to general surgery, gynecology, and more. Despite initial concerns over costs and the learning curve, the benefits in terms of reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker returns to normal activities have solidified their place in modern healthcare.
Alongside robotic systems, intraoperative imaging and navigation technologies have also seen significant advancements. Devices such as the O-arm Surgical Imaging System have revolutionized the way surgeries, particularly spinal and neurosurgical procedures, are performed. This technology provides real-time, 3D imaging that enables surgeons to precisely navigate surgical instruments, improving surgical accuracy and patient safety.
Furthermore, automation has found a place in anesthesia administration as well. Automated Anesthesia Delivery Systems (AADS) use complex algorithms and sensors to monitor and regulate the delivery of anesthetic agents during surgery, thereby reducing the risk of human error and providing a more consistent level of sedation.
In recent years, we’ve also witnessed the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the operating room. AI can assist in preoperative planning by predicting potential complications and outcomes based on a wealth of patient data. During surgery, AI can aid in real-time decision making and even direct robotic systems to perform certain tasks, thus enhancing the surgeon’s capabilities.
Additionally, AI-powered predictive analytics can help manage surgical workflows, optimize resource allocation, and even predict patient recovery times, leading to improved operational efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Despite these advancements, it’s important to remember that automation is a tool to aid human practitioners, not replace them. These technologies require human oversight for optimal use and to manage unexpected situations that may arise.
In conclusion, advancements in automation have revolutionized the operating room environment, making surgeries safer, more efficient, and less invasive. As we move forward, further research and development are needed to overcome existing challenges and harness the full potential of these technologies. This is indeed an exciting time for medicine, as we stand on the brink of even more revolutionary advancements in surgical automation.